Cruciate Ligament Rupture in Dogs: latest treatment techniques and the Role of INDIBA
Published:17 May,2023
Marina Rodriguez Alonso | Veterinarian, master in equine physiotherapy | Global Brand Manager INDIBA Animal Health
Small animals veterinarians know very well that springtime is the “cruciate ligament rupture” season. CLR is a common orthopedic injury that affects a significant number of dogs worldwide, particularly in certain breeds. It is estimated that around 1 in 100 dogs experiences this debilitating injury during their lifetime. Large and giant breed dogs, such as Labrador Retrievers, Golden Retrievers, and German Shepherds, are more susceptible to cruciate ligament rupture due to their size and structural predisposition.
When it comes to treating cruciate ligament rupture, veterinarians have several options to consider based on the severity of the injury and the individual patient. Conservative management, which involves rest, anti-inflammatory medications, and physical therapy, may be suitable for small dogs or those with partial tears. However, most cases of complete tears require surgical intervention. Traditional surgical techniques, such as TPLO (tibial plateau leveling osteotomy) and extracapsular repair, have shown good outcomes in restoring stability to the knee joint.
But what are the most recent updates in the treatment of CLR? Let’s review them.
Advanced surgical techniques: the most common techniques currently used by vet surgeons are the Tibial Plateau Levelling Osteotomy (TPLO) and the Tibial Tuberosity Advancement (TTA), which have been perfected over the years. Another technique that are not so new but is being researched and improved lately is the Modified Maquet Procedure (MMP). More advanced surgical techniques and materials are under research and development as well, and these include new intra-articular ligament repair techniques and the use of newer and biocompatible replacement materials and implants, which we mention further below.
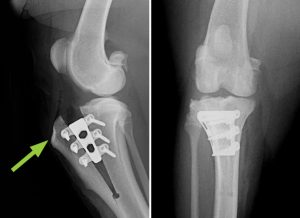 TTA Surgery for Cruciate Ligament Rupture (Image; North Downs Specialist Referrals)
TTA Surgery for Cruciate Ligament Rupture (Image; North Downs Specialist Referrals)
Arthroscopy: Arthroscopy, a minimally invasive procedure, has gained popularity in the treatment of cruciate ligament rupture. It allows for direct visualization of the joint, assessment of ligament integrity, and concurrent treatment of any associated intra-articular conditions. Arthroscopic-assisted techniques can facilitate more precise ligament repair or reconstruction.
Biomaterials and implants: The use of biomaterials and implants has shown promise in improving surgical outcomes. Advanced materials, such as synthetic ligaments, bioabsorbable implants, and tissue scaffolds, aim to provide support during the healing process and enhance long-term stability of the joint. These technologies are still being researched and refined, and their efficacy is evolving.
Regenerative medicine: Emerging regenerative medicine techniques, including platelet-rich plasma (PRP) and stem cell therapy, hold promise for promoting tissue healing and reducing inflammation in cruciate ligament injuries. These therapies aim to accelerate the repair process, enhance tissue regeneration, and improve long-term outcomes. Research in this area is ongoing, and their specific role in cruciate ligament rupture treatment is still being explored.
Rehabilitation and physical therapy: The importance of rehabilitation and physical therapy in the treatment of cruciate ligament rupture has gained recognition over the last few years. Rehabilitation protocols tailored to individual dogs can help improve muscle strength, joint range of motion, and overall function. Techniques such as underwater treadmill therapy, electrotherapy (such as laser therapy and radiofrequency), and therapeutic exercises play a vital role in post-operative rehabilitation.
The Role of INDIBA in the CLR treatment and recovery:
 INDIBA, a non-invasive radiofrequency device, has emerged as a valuable tool for enhancing recovery and rehabilitation in dogs with cruciate ligament rupture. Our innovative therapy promotes tissue healing, reduces inflammation, and accelerates the recovery process. INDIBA works by increasing local blood flow, enhancing cellular metabolism, and stimulating the body’s natural regenerative processes. It can be used both after surgery and as a complement to conventional treatment.
INDIBA, a non-invasive radiofrequency device, has emerged as a valuable tool for enhancing recovery and rehabilitation in dogs with cruciate ligament rupture. Our innovative therapy promotes tissue healing, reduces inflammation, and accelerates the recovery process. INDIBA works by increasing local blood flow, enhancing cellular metabolism, and stimulating the body’s natural regenerative processes. It can be used both after surgery and as a complement to conventional treatment.
The benefits of INDIBA for dogs recovering from cruciate ligament rupture are multifold. It aids in reducing pain and swelling, improving range of motion, and accelerating tissue healing. The therapy is non-painful, non-invasive, and well-tolerated by dogs, making it an attractive option for veterinarians and pet owners alike. INDIBA can be easily incorporated into existing rehabilitation protocols, providing a complementary approach to conventional therapies such as physical therapy, hydrotherapy, and therapeutic exercises.
IMPORTANT: All diagnostics and treatments of injuries and diseases in animals must be done by an animal health professional.
Do you want to try INDIBA?
Contact a Product Expert
Sources:
- Innovative, intra-articular, prosthetic technique CCL reconstruction in dogs
- Surgical treatment of CCL disease in dogs using TPLO or TTA
- Outcome of CCL replacement with an enhanced polyethylene terephthalate implant in the dog
- Outcome after MMP in dogs with unilateral CCLR